Gastric Sleeve vs. Gastric Bypass: Which One Is Right for You?
As a Bariatric Surgeon, I’ve witnessed firsthand how profoundly obesity can affect a person’s health and overall well-being. It’s more than just a weight issue—it’s a chronic condition that puts millions of people worldwide at risk for serious health problems, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
Bariatric surgery in Bogotá offers a proven path to long-term, sustainable weight loss. More importantly, it can significantly reduce the risk of obesity-related health complications and help patients reclaim a fuller, healthier life.
Why Addressing Obesity Matters
Obesity is a medical condition marked by an excessive amount of body fat, often defined by a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 or higher. But it’s not just about numbers on a scale—it’s a complex disease influenced by a range of factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle choices.
If you’re considering a surgical solution to weight loss, understanding your options is the first step toward lasting change. Two of the most recommended procedures are Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass. While both are highly effective, they work in different ways and may be better suited to different health profiles and personal goals.
In our practice, we focus on helping patients make informed decisions that align with their unique needs, health history, and long-term vision for wellness.
Health Risks Associated with Obesity
Living with obesity doesn’t just affect how you feel day to day—it can have serious long-term consequences for your overall health. Here are some of the most common and concerning conditions linked to excess weight:
Heart Disease and High Blood Pressure
Carrying excess weight puts added strain on your heart. As your body grows larger, your heart has to work harder to pump blood, often leading to high blood pressure (hypertension). Obesity is also closely tied to elevated cholesterol and triglyceride levels, which can cause plaque buildup in the arteries—a condition known as atherosclerosis. Over time, this significantly raises the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Type 2 Diabetes
Fat stored around the abdomen can interfere with how your body uses insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. This insulin resistance can lead to persistently high blood sugar levels, eventually resulting in type 2 diabetes. It’s one of the most common—and most serious—conditions associated with obesity.
Sleep Apnea and Breathing Issues
Extra fat around the neck and upper body can compress your airways, especially when lying down. This often leads to sleep apnea—a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during the night. It not only affects sleep quality but can also increase the risk of heart problems and fatigue during the day.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
In people with obesity, the liver tends to store excess fat, which can trigger inflammation and scarring. Left untreated, this can progress to more serious liver damage, including cirrhosis. NAFLD often develops silently, without symptoms, making regular checkups and early intervention especially important.
Joint Pain and Osteoarthritis
Excess weight puts continuous pressure on the joints, particularly the knees, hips, and lower back. Over time, this added stress accelerates the breakdown of cartilage—the cushioning tissue that protects your joints—leading to osteoarthritis, stiffness, and chronic pain.
Increased Cancer Risk
Obesity can create a hormonal imbalance that may increase the risk of certain cancers. Higher levels of estrogen and other hormones associated with excess fat can stimulate the growth of tumors. Obesity has been linked to cancers of the breast, colon, kidney, and more.
At our practice, we believe that understanding these risks is the first step toward making empowered, life-changing decisions. Whether you’re exploring bariatric surgery or other solutions, we’re here to help guide you toward a healthier, more confident future.
What Is Bariatric Surgery?
Bariatric surgery is one of the most effective medical treatments available for addressing obesity and the serious health risks that come with it. At its core, bariatric surgery involves reducing the size of the stomach, which limits how much food you can eat and helps trigger significant, long-term weight loss.
But the benefits go far beyond the number on the scale. Bariatric surgery has been shown to dramatically improve—or even resolve—many weight-related health issues, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and joint pain.

Patients also report life-changing improvements in their overall well-being. Many feel more confident, energetic, and able to enjoy everyday activities without the limitations they once faced. In fact, the positive impact often extends to mental and emotional health, with many patients experiencing a noticeable decrease in symptoms of depression and anxiety.
In short, bariatric surgery is more than a weight loss procedure—it’s a powerful tool for reclaiming your health, your confidence, and your life.
Gastric Sleeve vs. Gastric Bypass: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to weight loss surgery, the two most performed procedures are the Gastric Sleeve and the Gastric Bypass. Both are highly effective tools for achieving significant weight loss and improving overall health, but they work in different ways and are suited to different types of patients.
What Is Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
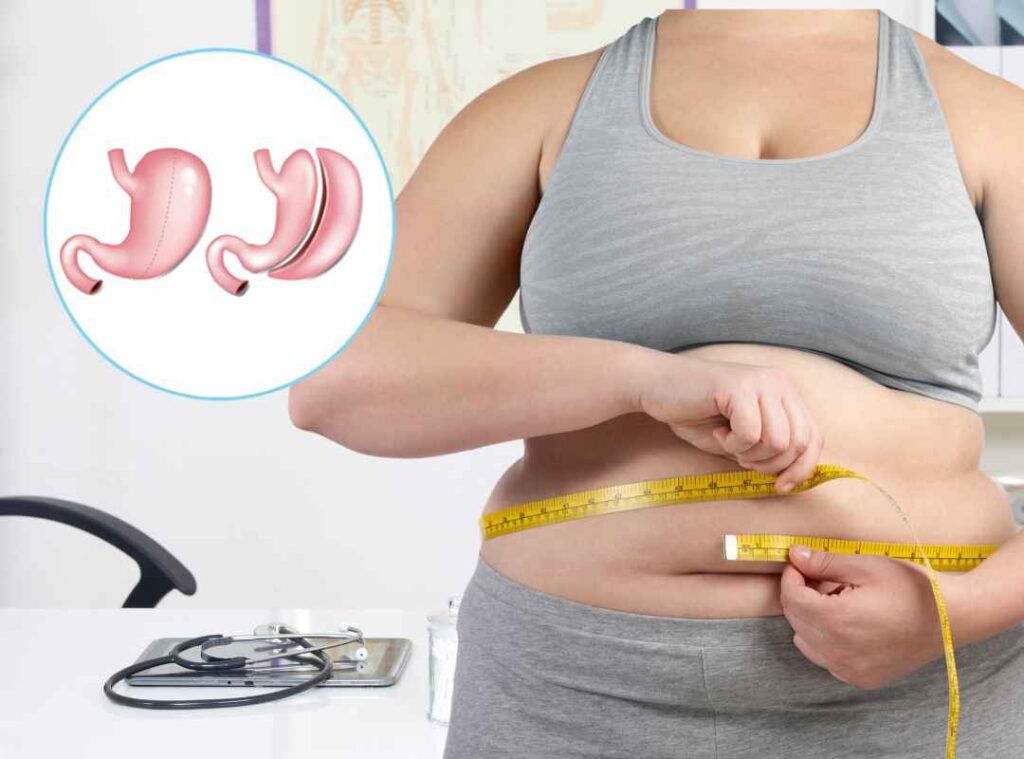

Also known as sleeve gastrectomy, this procedure involves removing approximately 75% of the stomach to create a smaller, sleeve-shaped stomach. With a reduced stomach size, patients feel full with less food, leading to substantial and sustained weight loss.
One of the key benefits of the gastric sleeve is that it does not involve altering the intestines, so your body still absorbs nutrients as it normally would. This makes it a simpler, less invasive procedure compared to gastric bypass, with fewer risks of nutritional deficiencies.
What Is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
In gastric bypass—also called Roux-en-Y gastric bypass—the surgeon creates a small pouch at the top of the stomach and connects it directly to a section of the small intestine. This reroutes food so it bypasses most of the stomach and part of the intestine, reducing both the amount of food you can eat and the number of calories and nutrients your body absorbs.
Gastric bypass is especially effective for patients with more severe obesity or weight-related conditions like type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure. However, because it’s more complex, it does come with a slightly higher risk of complications and requires more careful long-term nutritional management.
Choosing the Right Option for You
Both procedures are powerful tools in the fight against obesity, but they’re not one-size-fits-all. In general:
- Gastric Sleeve is less invasive and may be better suited for patients with moderate obesity or those seeking a lower-risk option.
- Gastric Bypass offers more dramatic weight loss and metabolic benefits, especially for patients with significant obesity or conditions like diabetes—but it involves a more complex surgery.
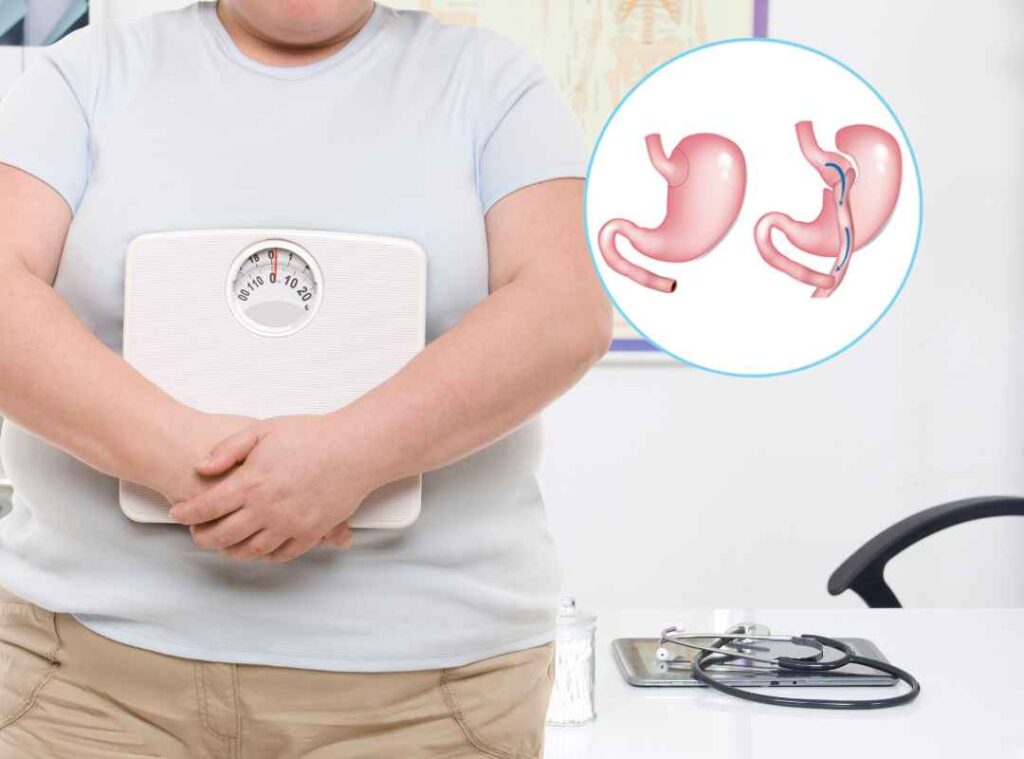
The best choice depends on your individual health profile, goals, and the recommendation of your bariatric surgeon. At our practice, we take the time to understand your needs and guide you through every step of the decision-making process, helping you choose the path that offers the best chance for lasting results and a healthier future.
5 Key Differences Between Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass Surgery
If you’re considering weight loss surgery, understanding how gastric sleeve and gastric bypass differ can help you make an informed decision. While both are effective for long-term weight loss and improving obesity-related health conditions, they differ in several important ways:
1. Surgical Procedure
Gastric Sleeve
Involves removing about 75–80% of the stomach, leaving a narrow, sleeve-shaped stomach. The intestines remain untouched.
Gastric Bypass
A small pouch is created at the top of the stomach and connected directly to the small intestine, bypassing a significant portion of the digestive tract.
Key Difference: The sleeve is less invasive and doesn’t involve rerouting the intestines, while the bypass requires a more complex reconstruction of the digestive system.
2. How Weight Loss Is Achieved
Gastric Sleeve
Limits the amount of food you can eat and reduces hunger by lowering the production of ghrelin, the hormone responsible for appetite.
Gastric Bypass
Combines food restriction with reduced nutrient absorption (malabsorption) by bypassing part of the small intestine.
Key Difference: The sleeve relies solely on portion control and appetite reduction, while the bypass adds a malabsorptive component for enhanced weight loss.
3. Who It’s Best For
Gastric Sleeve
Typically recommended for patients with a BMI between 30 and 40, and those without severe metabolic conditions.
Gastric Bypass
Ideal for patients with a BMI over 40 or for those with serious obesity-related issues like uncontrolled type 2 diabetes or severe acid reflux.
Key Difference: Bypass is generally preferred for patients with more advanced obesity or complex medical conditions.
4. Surgery & Recovery Time
Gastric Sleeve
Shorter surgery time (1–2 hours) and usually a faster initial recovery.
Gastric Bypass
Longer procedure (2–3 hours) and a more extended recovery due to its complexity.
Key Difference: The sleeve is quicker to perform and may offer a smoother early recovery process.
5. Nutritional Impact
Gastric Sleeve
Does not interfere with nutrient absorption, so the risk of deficiencies is lower.
Gastric Bypass
Alters how nutrients are absorbed, increasing the risk of deficiencies in iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and others—requiring lifelong supplements.
Key Difference: Patients undergoing bypass need to be more vigilant about nutrition and committed to ongoing supplementation.
Both procedures have helped countless patients regain control of their health, but the right choice depends on your individual needs, medical history, and lifestyle. At our clinic, we’ll work closely with you to evaluate which option aligns best with your long-term goals and ensures your safety, success, and satisfaction.

Preparing for Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery is a life-changing step—and preparation is key to long-term success. Before the procedure, every patient undergoes a comprehensive health evaluation to ensure they’re physically and mentally ready for surgery. This includes a full medical history, physical examination, psychological assessment, and nutritional counseling.
In addition to these evaluations, patients are encouraged to start making important lifestyle changes. This may involve adopting a healthier diet, introducing regular physical activity, and quitting smoking if applicable. These habits not only help prepare the body for surgery but also set the foundation for a smoother recovery and more sustainable results.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
No matter which type of bariatric surgery you choose, recovery doesn’t stop when you leave the operating room. A detailed post-operative care plan is essential for healing and long-term success. This includes:
- Following a specialized diet that transitions from liquids to soft foods, and eventually to solid meals.
- Taking prescribed medications and nutritional supplements as directed.
- Attending all follow-up appointments with your surgeon and care team to monitor progress and address any concerns.
What to Expect After Bariatric Surgery

Bariatric surgery triggers profound changes in the body—and in your lifestyle. Most patients experience rapid weight loss in the first few months, along with a noticeable decrease in appetite. There will also be changes in how your body absorbs nutrients, which is why lifelong attention to nutrition and supplementation is so important.
But beyond physical transformation, patients often report a boost in energy, self-confidence, and quality of life. It’s important to understand that surgery is just one part of the journey. Long-term success comes from embracing new habits, staying consistent with follow-up care, and being fully committed to your health goals.
At our practice, we’re here to support you every step of the way—from your first consultation through your transformation and beyond.
Exercise and Nutrition After Bariatric Surgery
Long-term success after bariatric surgery isn’t just about the procedure—it’s about adopting a healthy, sustainable lifestyle. Both physical activity and nutrition play a critical role in helping patients maintain weight loss, preserve muscle mass, and support overall well-being.
Personalized Fitness Plans
Every post-bariatric patient has different physical abilities, so exercise plans should be tailored to individual needs. In the early stages, low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or gentle yoga are ideal for building endurance and improving mobility. As the body adjusts and strength improves, patients can gradually incorporate more intensity and resistance training to enhance muscle tone and metabolic health.
Nutrition That Supports Healing and Health
Nutritional care after bariatric surgery is just as important as physical activity. Patients need a well-balanced eating plan that meets their new metabolic needs. This typically includes:
- A diet high in lean protein to preserve muscle mass
- Plenty of fiber for digestive health
- Reduced carbohydrates and fats to support weight loss
- Daily supplements of essential vitamins and minerals, especially for gastric bypass patients, whose nutrient absorption is reduced
Ongoing support from a registered dietitian or nutritionist is often helpful to ensure patients stay on track and avoid nutritional deficiencies.
Gastric Sleeve vs. Gastric Bypass: A Personalized Choice
Gastric sleeve and gastric bypass remain the two most popular bariatric procedures, each with unique benefits and considerations. Choosing the right one is never a one-size-fits-all decision, it’s a deeply personal process guided by medical expertise and the patient’s individual needs.
Here’s how bariatric specialists determine the best surgical option:
Body Mass Index (BMI)
BMI helps define the level of obesity and guides treatment options. Gastric bypass may be preferred for patients with higher BMIs or more complex weight issues, while the sleeve can be a great fit for moderate obesity.
Metabolic Conditions and Comorbidities
Health conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea often influence the choice. Bypass surgery, with its hormonal and metabolic impact, can be especially effective in resolving or improving these issues.
Medical and Surgical History
Previous abdominal surgeries, acid reflux, or other health concerns play a major role in the decision. The gastric sleeve, being less invasive, is sometimes the safer choice for patients with a complex medical background.
Expert Medical Evaluation
Ultimately, the bariatric surgeon’s assessment is key. Your specialist will conduct thorough exams, lab work, and metabolic studies to recommend the most appropriate and safest procedure for your long-term health.
A Life-Changing Journey with the Right Support
No matter which paths you take—gastric sleeve or gastric bypass—success depends on preparation, dedication, and the right medical guidance. With a commitment to lifestyle changes and support from a trusted care team, bariatric surgery can be a powerful, life-transforming solution for those struggling with obesity. We’re here to walk that journey with you—every step of the way.
Not Sure Which Bariatric Surgery Is Right for You?
Choosing the right bariatric procedure is a big decision—and one that should be made with expert guidance. In a personalized consultation with me, Dr. Rubén Luna, we’ll take a close look at your health history, your goals, and your individual needs to determine whether Gastric Sleeve or Gastric Bypass is the best option for you.
Every patient is unique, and my priority is to help you take that first step with confidence toward a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Schedule your consultation today, let’s find the right solution together and start your journey toward lasting wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions: Gastric Sleeve vs. Gastric Bypass
Are Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass reversible?
Not really. Gastric sleeve surgery is permanent because it involves removing a large portion of the stomach. Gastric bypass, while technically reversible through a complex surgery, is not commonly reversed due to potential risks and complications. Both procedures are considered lifelong changes.
Which procedure has more long-term dietary restrictions?
Gastric bypass typically requires more long-term dietary adjustments due to reduced nutrient absorption. Patients must be especially mindful of vitamin and mineral intake, particularly iron, calcium, and B12. While the sleeve doesn’t affect absorption, a balanced diet and good nutritional habits are still essential for lasting results.
Which surgery is more effective at controlling hunger?
Both surgeries help reduce hunger, but through different mechanisms. Gastric sleeve surgery lowers levels of ghrelin, the hormone that triggers hunger, because the part of the stomach that produces it is removed. Gastric bypass also affects hunger by altering gut hormones. The right choice depends on your specific hunger patterns and health profile.
Will I need to take vitamin supplements for life?
Yes—especially after gastric bypass, where nutrient absorption is significantly reduced. Supplementation is essential to prevent deficiencies. With gastric sleeve, supplementation may also be necessary, particularly in the early years post-op, but the risk of deficiency is generally lower.
Do these surgeries affect mental health?
They often have a positive impact—boosting self-esteem, improving mood, and reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. However, adapting to lifestyle changes, body image shifts, and a new relationship with food can be emotionally challenging. Ongoing psychological support is strongly recommended, regardless of the procedure.
Which is better for patients with severe acid reflux?
Gastric bypass is usually the better option for those suffering from severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), as it can significantly reduce reflux symptoms. On the other hand, gastric sleeve may worsen acid reflux due to increased pressure in the smaller stomach.
Which procedure is more suitable for someone planning a future pregnancy?
Both surgeries can be safe for women who plan to get pregnant, but careful planning is essential. It’s typically recommended to wait 12 to 18 months after surgery before conceiving. Gastric bypass patients will require closer nutritional monitoring during pregnancy due to malabsorption risks.
How soon can I return to work after surgery?
Recovery times vary, but most gastric sleeve patients can return to work in 2 to 4 weeks. Gastric bypass may require a bit more recovery, usually 3 to 6 weeks—depending on how the patient heals and the physical demands of their job.
Can I drink alcohol after bariatric surgery?
Alcohol should be avoided, especially during the early recovery period. After surgery, alcohol is absorbed more rapidly, leading to stronger effects and potential harm to the digestive system. This is particularly risky with gastric bypass due to altered absorption. If alcohol is reintroduced later, it should be done cautiously and with your doctor’s approval.
Are the results permanent?
They can be—but they’re not guaranteed. Long-term success depends on a lifelong commitment to healthy habits, including diet, exercise, and regular medical follow-ups. Without this dedication, weight regain is possible with either procedure.